How to run OpenFaaS on AWS Fargate with economical, auto-scaling containers. A low friction AWS native deployment using VPCs, ECS, security groups, ALBs, AWS Secrets Manager and AWS Route 53 for DNS, load-balancing and service discovery.
Experience required:
- Basic-level OpenFaaS
- Intermediate-level AWS
This article will explain why I’ve chosen to run OpenFaaS on AWS Fargate. We then move on to explore how to deploy a fully working environment and run our first function.
For me, one of the best things about OpenFaaS is how portable it is. You can run OpenFaaS out of the box using officially supported platforms like Kubernetes and Docker Swarm . The community has added many other platforms, that allow you to run OpenFaaS in more places. A good example of this is deploying OpenFaaS on Hashicorp’s nomad application scheduler.
Why use AWS Fargate?
Your reasons for choosing AWS Fargate are likely to vary depending on your experience, knowledge and goals. At form3 we use AWS ECS to schedule Docker containers. We decided to build an OpenFaaS provider to run on ECS so we could leverage all of our existing knowledge and infrastructure code. Perhaps you too work in a team that uses AWS ECS? You may also work in a company that hasn’t adopted Kubernetes and doesn’t plan to in the immediate future. So if you fit that in that camp, how do you leverage the advantage of serverless computing? A good choice would be to look at a managed serverless platform like AWS Lambda. In this article we examine another option, running OpenFaaS on Fargate, which I believe gives you some of the benefits of a managed service like Lambda with the flexibility of an open-source serverless platform like OpenFaaS.
Architecture
OpenFaaS functions are built as Docker images and deployed as Docker containers. This approach may be very familiar to
developers using microservices. The platform is composed of gateway, provider and monitoring components. The
gateway delegates the deployment and invoking of functions to the provider. The provider in our case is faas-fargate,
which has been specifically designed to run and invoke functions using AWS Fargate containers.
The diagram below shows how each of these components interact:
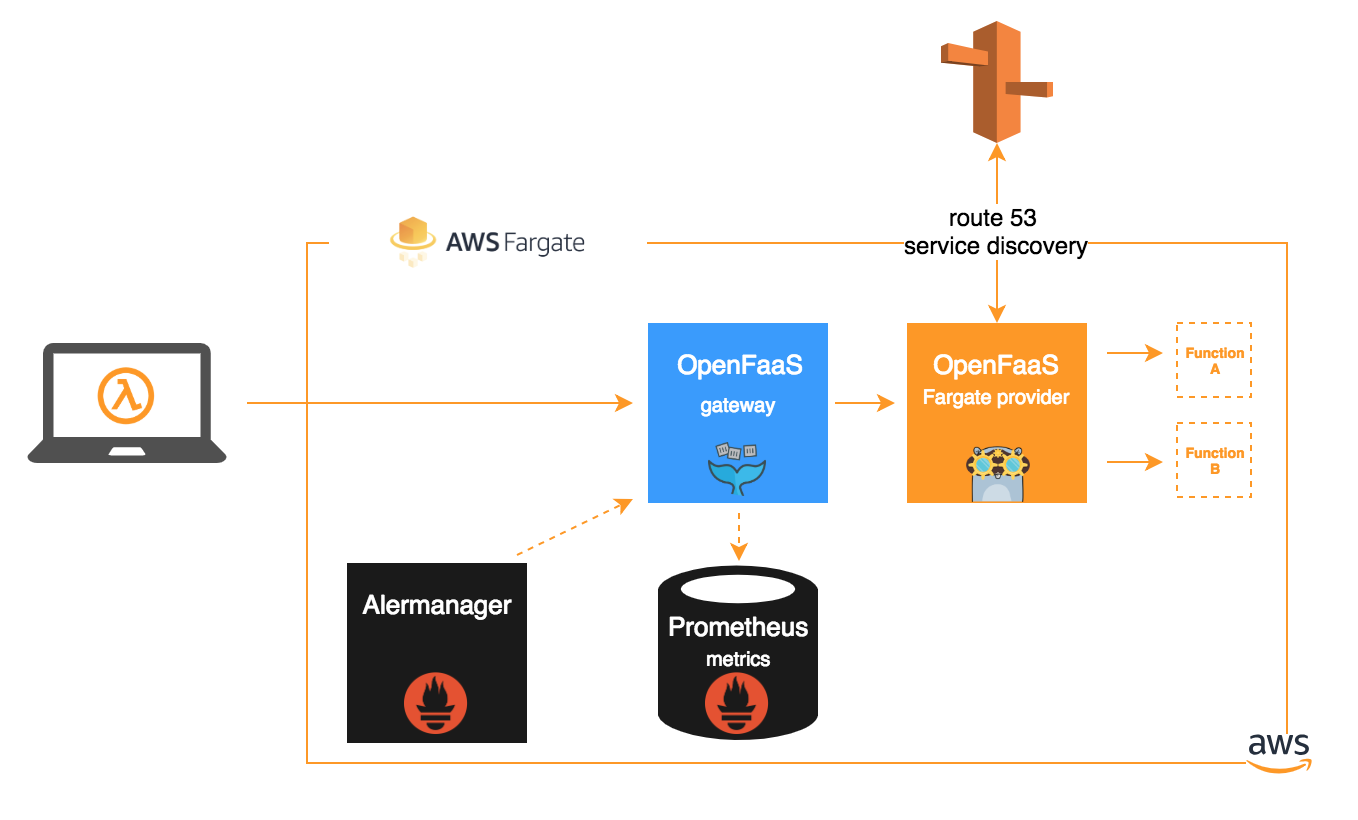
Each of the components are created and deployed as Fargate containers.
Architecture features:
- [networking] we restrict traffic between containers using AWS security groups
- [networking] ingress traffic from the Internet is terminated in a
public subnet. Container workloads are scheduled in aprivate subnetthat has no access to the Internet - [discovery] all workloads use Amazon Route 53 auto naming to manage service registration / de-registration
- [logging] we configure each container workload to log to AWS cloudwatch.
- [secrets] managed using AWS Secrets Manager and assigned access to functions
in the
stack.yaml - [tls] ingress TLS is automatically provisioned using Certbot and the Let’s Encrypt certificate authority.
Run OpenFaaS on Fargate
The easiest way to run OpenFaaS on Fargate is to use the terraform module I developed to deploy all the necessary components:
Simply run the following commands:
Disclaimer: as you would expect creating resources in AWS will incur charges. Please follow the tear-down instructions below when you have finished.
Mac
$ brew install terraform # or upgrade
git clone https://github.com/ewilde/terraform-aws-openfaas-fargate
cd terraform-aws-openfaas-fargate
cat > ./terraform.tfvars <<EOF
acme_enabled = "1"
acme_email_address = "my@certbot-account-email.com"
alb_logs_bucket = "my-logs"
aws_region = "eu-west-1"
debug = "0"
developer_ip = "31.53.195.58"
route53_zone_name = "openfaas.my-domain.com"
self_signed_enabled = "0"
EOF
terraform apply
Linux
$ wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.11.7/terraform_0.11.7_linux_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_0.11.7_linux_amd64.zip
sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin
git clone https://github.com/ewilde/terraform-aws-openfaas-fargate
cd terraform-aws-openfaas-fargate
cat > ./terraform.tfvars <<EOF
acme_enabled = "1"
acme_email_address = "my@certbot-account-email.com"
alb_logs_bucket = "my-logs"
aws_region = "eu-west-1"
debug = "0"
developer_ip = "31.53.195.58"
route53_zone_name = "openfaas.my-domain.com"
self_signed_enabled = "0"
EOF
terraform apply
Configuration options explained
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| acme_enabled | (Recommended)1 to use the official acme terraform provider to create TLS certificates. Defaults to 0 |
| acme_email_address | (Recommended) Email address used to register TLS account, used in conjunction with acme_enabled |
| aws_region | (Required) The aws region to create the openfaas ecs cluster in |
| alb_logs_bucket | (Required) S3 bucket to store alb logs |
| debug | (Optional) 1 to create an ec2 bastion in the external subnet and a test instance in the internal subnet. Defaults to 0 |
| developer_ip | your IP address, used to whitelist incoming SSH to the bastion, debug is enabled |
| route53_zone_name | (Recommended) a Route 53 zone to create DNS records for the OpenFaaS gateway, i.e. openfaas.example.com, requires acme_enabled |
| self_signed_enabled | (Not recommended) Use a self-signed TLS certificate for the OpenFaaS gateway if not using acme_enabled. Defaults to 0 |
Once terraform has finished creating the resources you should see success message, which looks similar to:
Apply complete! Resources: 133 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
Outputs:
alb_uri = openfaas-1918537172.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com
bastion_ip = []
login = echo -n "t6UbsFKnjgtv4KLF3Uw5llN6fyONE6nV" | faas-cli login --gateway https://openfaas-1918537172.eu-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com --username=admin --password-stdin --tls-no-verify
login_secure = echo -n "t6UbsFKnjgtv4KLF3Uw5llN6fyONE6nV" | faas-cli login --gateway https://gateway.openfaas.12factor.io --username=admin --password-stdin
openfass_uri = https://gateway.openfaas.12factor.io/ui/
service_security_group = sg-0ff75545f2d542c4e
servicebox_ip = []
Verifying the installation
When the gateway is running you can start deploying and running functions.
You can tell if it’s ready by calling the healthz endpoint and waiting for a 200 http status code
$ curl https://openfaas.{your-domain}.com/healthz -i
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Length: 0
Date: Sat, 22 Dec 2018 10:39:17 GMT
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
You can also see the services running in the ECS console:
$ aws ecs list-services --cluster openfaas
{
"serviceArns": [
"arn:aws:ecs:eu-west-1:122668425727:service/gateway",
"arn:aws:ecs:eu-west-1:122668425727:service/prometheus",
"arn:aws:ecs:eu-west-1:122668425727:service/nats",
"arn:aws:ecs:eu-west-1:122668425727:service/alertmanager"
]
}
Deploying a function
We can deploy functions to AWS Fargate the same way we would with another other OpenFaaS provider, through the CLI, UI or REST API.
Let’s configure the faas-cli to point at our OpenFaaS cluster:
export OPENFAAS_URL=https://openfaas.{your-domain}.com
1. Lets create and deploy a function to our new stack using the CLI:
$ faas new hello-world --lang go -p ewilde
2018/12/22 10:29:03 No templates found in current directory.
2018/12/22 10:29:03 Attempting to expand templates from https://github.com/openfaas/templates.git
2018/12/22 10:29:05 Fetched 14 template(s) : [csharp dockerfile go go-armhf java8 node node-arm64 node-armhf php7 python python-armhf python3 python3-armhf ruby] from https://github.com/openfaas/templates.git
Folder: hello-world created.
___ _____ ____
/ _ \ _ __ ___ _ __ | ___|_ _ __ _/ ___|
| | | | '_ \ / _ \ '_ \| |_ / _` |/ _` \___ \
| |_| | |_) | __/ | | | _| (_| | (_| |___) |
\___/| .__/ \___|_| |_|_| \__,_|\__,_|____/
|_|
Function created in folder: hello-world
Stack file written: hello-world.yml
In the command above --prefix corresponds to my username on the Docker Hub.
The function will be built into a Docker image and then pushed there through the faas-cli up command.
You can also use your own self-hosted registry.
2. Open ./hello-world/handler.go to see the function entry point
package function
import (
"fmt"
)
// Handle a serverless request
func Handle(req []byte) string {
return fmt.Sprintf("Hello, Go. You said: %s", string(req))
}
3. Now let’s build and deploy the function to our new environment
$ faas up -f hello-world.yml
... <- lots of lovely build output from Docker
Successfully built f9833391f176
Successfully tagged ewilde/hello-world:latest
Image: ewilde/hello-world:latest built.
[0] < Building hello-world done.
[0] worker done.
[0] > Pushing hello-world [ewilde/hello-world:latest].
The push refers to repository [docker.io/ewilde/hello-world]
d1307abdafe5: Mounted from ewilde/hello-paris
9808cfceb9f2: Mounted from ewilde/hello-paris
a0db5d04a9ae: Mounted from ewilde/hello-paris
39c32d89aeac: Mounted from ewilde/hello-paris
c198ae36274e: Mounted from ewilde/hello-paris
b01940cbde37: Mounted from ewilde/hello-paris
df64d3292fd6: Mounted from ewilde/env
latest: digest: sha256:e0dbd58d58880e0771c3ab36cdcbd7a371fa80d91894f9e845f5f54132124586 size: 1785
[0] < Pushing hello-world [ewilde/hello-world:latest] done.
[0] worker done.
Deploying: hello-world.
Deployed. 202 Accepted.
URL: https://openfaas.{your-domain}.com/function/hello-world
Removing the installation
- Firstly, remove any functions that you have deployed using
faas-cli remove FUNCTION_NAME - Run
make destroy. This can take between 5-10 minutes. Thedestroytarget callsterraform destroy.
The
terraform destroycommand is used to destroy the Terraform-managed infrastructure.
$ make destroy
... <--- lots of destroying going on here
aws_subnet.external[2]: Destruction complete after 1m48s
aws_security_group.alb: Still destroying... (ID: sg-0a84a6bd951bacb6d, 1m50s elapsed)
aws_security_group.alb: Destruction complete after 1m51s
aws_vpc.default: Destroying... (ID: vpc-0220284dd7ba01f58)
aws_vpc.default: Destruction complete after 0s
Destroy complete! Resources: 133 destroyed.
Wrapping up
We’ve seen how the OpenFaaS provider architecture makes it easy to extend the platform and run serverless functions on AWS Fargate. Then we deployed a complete OpenFaaS stack using terraform on to AWS Fargate and secured the transport layer using the ACME provider and Let’s Encrypt.
My code:
- faas-fargate: OpenFaaS provider for AWS Fargate
- Terraform installer for faas-fargate: Installs the OpenFaaS platform for AWS Fargate using Terraform
What’s next for faas-fargate
- Support scale to zero using the faas-idler.
- Provide better observability for users and integrate Grafana with the standard deployment to surface function metrics.
Get connected
Get connected, ask questions, make comments and suggestions on:
New: Join the OpenFaaS #TeamServerless LinkedIn Group.

